The purpose of intercropping is to maximize the value of a given parcel of land – and value can come in many different forms.
In the context of cacao, intercropping is the act of integrating other trees and crops into a cacao plantation.
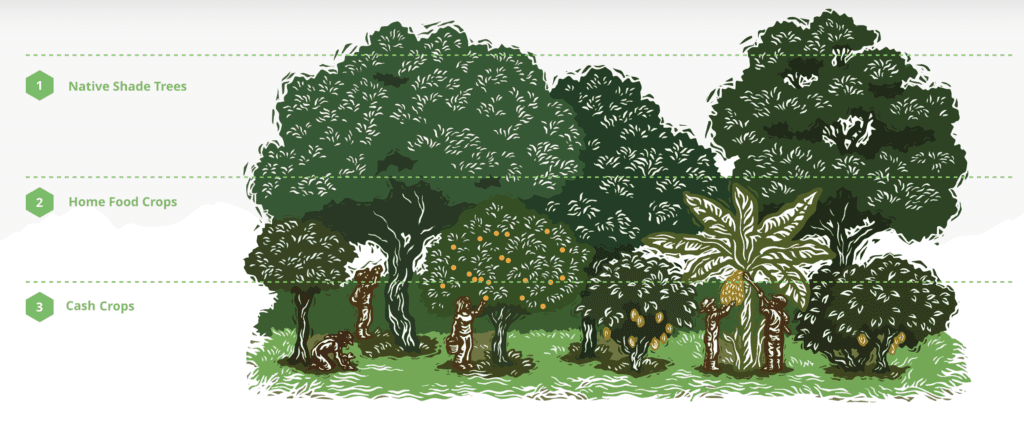
In some cases, this can mean planting rows of banana or fruit trees in between rows of cacao trees. In other cases, it can simply mean inserting shade trees every 10-25 meters, either in a grid pattern or as space and topography permit.
For example, integrating native shade trees into a cacao plantation increases CO2 removal, improves biodiversity, and can also increase the health of the cacao trees by protecting them from excessive sun.
Intercropping nitrogen-fixing trees can improve yields by enhancing soil fertility. Inserting fruit trees and banana plants can boost local food security and create additional revenue streams. Lemongrass intercropped on contour can prevent erosion, etc.
Próximamente versión en español
Entry added: November 2, 2022
Verified on: September 14, 2023
Authored By
Jerry Toth, Agroforestry practitioner, cacao grower, chocolate maker, based in Ecuador; TMA & To’ak Chocolate
Chocolate Maker
References
“What is Regenerative Agroforestry?” Third Millennium Alliance, May 21, 2021
